Understanding the Inner Workings of Livestreaming: Exploring the Camera-to-Stream Pipeline
In recent years, livestreaming has gained immense popularity, revolutionizing the way we consume and share content. From gaming sessions to concerts and educational seminars, livestreams have become an integral part of our digital landscape. But have you ever wondered how a livestream works behind the scenes? Let’s delve into the intricacies of the camera-to-stream pipeline, shedding light on the fascinating process that brings live video content to our screens.
The Camera: At the heart of any livestream is the camera. Modern livestreams can utilize a wide range of cameras, including professional-grade camcorders, DSLRs, mirrorless cameras, or even smartphones. The camera captures the video footage and serves as the primary source of content for the livestream.
Camera Setup and Configuration: Before the livestream begins, the camera must be properly set up and configured. This involves adjusting various settings such as resolution, frame rate, white balance, and focus to ensure optimal video quality. Additionally, audio setup is also crucial, as most livestreams incorporate audio alongside the video feed.
Capture Device: To bridge the gap between the camera and the computer, a capture device is employed. This device connects to the camera via HDMI, SDI, or other video output ports and converts the analog video signals into digital format that can be processed by the computer.
Encoding and Compression: Once the video signals are captured, they need to be encoded and compressed to reduce file size and make them suitable for streaming over the internet. The encoding process typically employs codecs such as H.264 or H.265, which compress the video while preserving a reasonable level of quality. This compression reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, ensuring smoother streaming and minimizing bandwidth requirements.
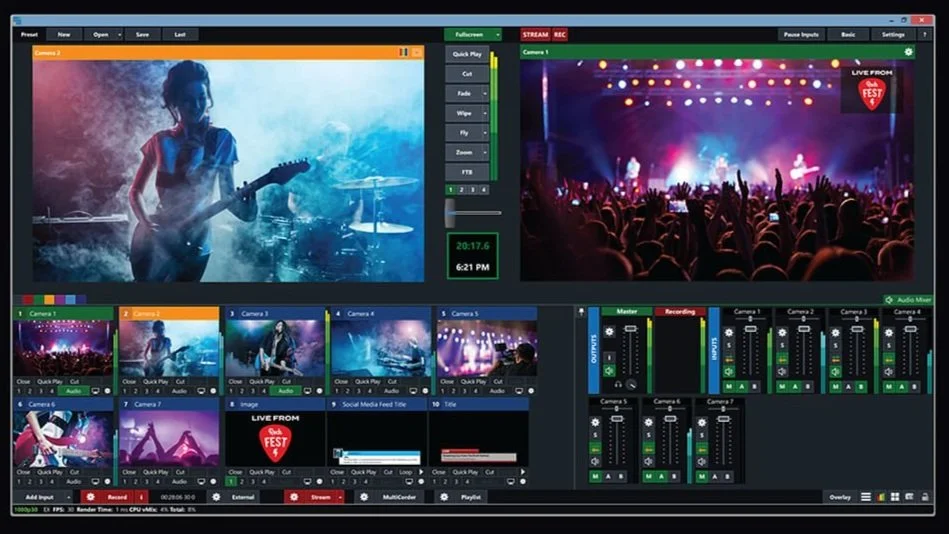
Streaming Software: Streaming software plays a crucial role in managing the camera feed, encoding, and transmitting the livestream. Popular streaming software options include OBS (Open Broadcaster Software), VMix, or specific software provided by livestreaming platforms like YouTube Live or Twitch. These software packages offer a range of features, including scene composition, overlays, adding text, switching between multiple cameras, and managing audio inputs.
Internet Connection: A stable and reliable internet connection is essential for livestreaming. The streaming software encodes the video feed into data packets, which are then transmitted over the internet to streaming platforms or content delivery networks (CDNs). The upload speed of the internet connection directly impacts the quality and smoothness of the livestream. Higher upload speeds are necessary for streaming at higher resolutions and bitrates.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs play a crucial role in ensuring that livestreams are delivered efficiently to viewers. CDNs consist of distributed servers strategically located worldwide. When a viewer requests the livestream, the CDN automatically determines the closest server and delivers the video data from that server. This reduces latency and improves the overall viewing experience by minimizing buffering and stream interruptions.
Viewing the Livestream: Once the livestream data reaches the viewer, their device decodes and decompresses the video feed, making it playable on their screen. The viewer can watch the livestream on various devices such as smartphones, tablets, computers, or smart TVs, provided they have a compatible media player or livestreaming app.
Livestreaming has transformed the way we engage with live content, offering real-time experiences from the comfort of our screens. Understanding the camera-to-stream pipeline allows us to appreciate the intricate processes involved in bringing a livestream to life. From camera setup to encoding, internet transmission, and content delivery, each step contributes to delivering seamless and captivating livestreams. So, the next time you tune into a livestream, take a moment to appreciate the complex behind-the-scenes operations that make it all possible. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative developments in the livestreaming space, further enhancing the quality and accessibility of live content.